An Easy Guide to Amazon S3 Minio Go (Golang) V7 on Titan Cloud Storage
The MinIO Go SDK is a software development kit that lets developers use the Go programming language to connect to and work with the Amazon S3-compatible Titan Cloud Storage service. The SDK gives you a simple, easy-to-understand way to create and manage buckets, upload and download objects, and set access policies. It also offers server-side encryption, multipart uploads, and more. The Minio Go SDK makes adding Titan Cloud Storage to your Go-based apps easy and flexible.
This quick start guide will show you how to install the Go SDK and run a few basic Go program examples.
Prerequisites
Prerequisites required are as follows:
- Go programming language
- Minio Go SDK package.
Goals
After finishing this article, you'll be able to:
- Initialize Titan cloud instance.
- Create a new bucket with a specified name.
- Checking if the bucket exists.
- Delete an existing bucket
- Retrieve a list of all buckets in the account.
- Upload a new object to a bucket or replace an existing object with a new version.
- Retrieve an object from a bucket and download it to a local machine.
- Delete an object from a bucket.
- Delete many objects from a bucket.
- Retrieve a list of objects within a bucket.
- Make a copy of an existing object within the same bucket or in a different bucket.
- Check if an object exists in a bucket or not.
- Uploads a file to a bucket.
- Downloads an object from a bucket to a file.
How do I use minio for Go (Golang) with Titan Cloud Storage
Here are the steps to use Go SDK for Amazon S3 Titan Cloud Storage:
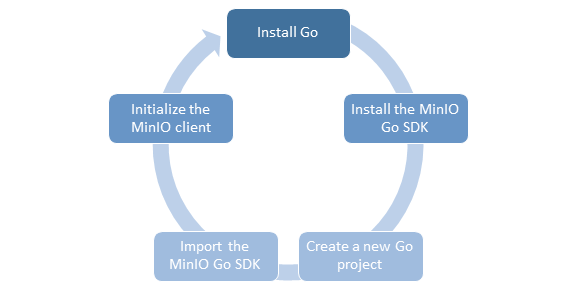
Step 1. Install Go on your system.
• Download and install the Go programming language from the official website at
https://go.dev/doc/install
• To confirm the installation, In Windows, click the Start menu.
• In the menu's search box, type cmd, then press the Enter key.
• Type the following command on cmd.
$ go version

• You're all set to start!
Step 2. Get started with Go
You can start with simple Go code by following steps.
• Create a new Go project. Open a command prompt and make a directory.
mkdir Go-Code
cd Go-Code
We have created a directory on Desktop named “Go-Code”.

For more help, you can also visit https://go.dev/doc/tutorial/getting-started
Step 3. Install the MinIO Go SDK
• Open a command prompt and install the MinIO Go SDK using the following command:go get -u github.com/minio/minio-go/v7
Step 4. Initialize Go project
Run the go mod init command and give it the module's name, which your code will be in. It will create a go.mod file that will track dependencies. The name is the path to the module.
• Initialize it with the following command:
Run the go mod init command and give it the module's name, which your code will be in. It will create a go.mod file that will track dependencies. The name is the path to the module.
• Initialize it with the following command:go mod initFor Example:go mod init examples/create_connection

Note: A go.mod file that keeps track of the modules that provide those packages defines that module. When your Go example imports packages from other modules, you take care of these dependencies through the module that contains your code. The go.mod file stays with your code, including in your source code repository.
For detail understanding please visit: https://go.dev/ref/mod#go-mod-init
Step 5. Initialize the Minio client and run Go code
• Open text editor, create a file create_connection.go in which to write your code. Paste the following code into your create_connection.go file and save the file.
Go example:
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"github.com/minio/minio-go/v7"
"github.com/minio/minio-go/v7/pkg/credentials"
)
func main() {
// Initialize titan client object with an endpoint, access key, and secret key.
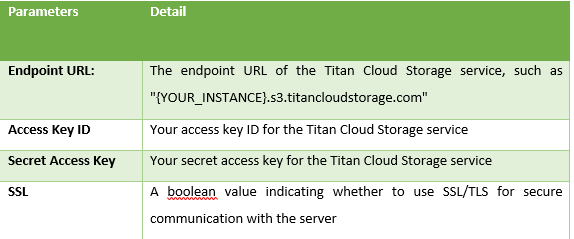
endpoint := "{YOUR_INSTANCE}.s3.titancloudstorage.com"
accessKey := ""
secretKey := ""
useSSL := true
region := "us-west-1"
// Initialize titan client object.
titan_obj, err := minio.New(endpoint, &minio.Options{
Creds: credentials.NewStaticV4(accessKey, secretKey, ""),
Secure: useSSL,
Region: region,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
fmt.Printf("Connection created successfully!
")
// Specify the name of the bucket to create.
bucketName := "my-bucket"
// Check if the bucket already exists.
found, err := titan_obj.BucketExists(context.Background(), bucketName)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
if found {
fmt.Printf("Bucket '%s' already exists!
", bucketName)
return
}
}Instance parameters
We have initialized the client ‘titan cloud storage’ in above code by creating a new titan_obj object with the following parameters:
• Run your Go code example.$ go run .
• Output:

That's it! You can now use the MinIO Go SDK to interact with Amazon S3 Titan Cloud Storage service.
Quick Start Examples
With the MinIO Go SDK, developers can quickly and easily build powerful applications that use Titan Cloud Storage's features and take advantage of the Go programming language's ease of use and flexibility. Developers can use the SDK to do many different things with Titan Cloud Storage, like creating and deleting buckets, uploading and downloading objects, and managing bucket policies and metadata.
Bucket operations
Bucket operations are operations that can be performed on buckets in cloud object storage services such as MinIO, Amazon S3, and Google Cloud Storage. Some common bucket operations include:
- Create bucket: Create a new bucket with a specified name.
- Delete bucket: Delete an existing bucket.
- List buckets: Retrieve a list of all buckets in the account.
- Get bucket location: Retrieve the geographic location of a bucket.
- Get bucket object count: Retrieve the number of objects in a bucket.
- Get bucket size: Retrieve the total size of all objects in a bucket.
- These operations can be performed using the API provided by the cloud object storage service or using client libraries like MinIO Go. We will see few operations below with code examples and explanation.
1. Initializes a new Titan Cloud Connection Code:
The below code snippets Initializes a new Titan Cloud object storage client.
General Method:
New(endpoint string, opts Options) (Client, error)
The method takes the following parameters:
Code File:package main
import (
"log"
"github.com/minio/minio-go/v7"
"github.com/minio/minio-go/v7/pkg/credentials")
func main() {
// Set up credentials and endpoint for Titan Cloud Storage.
endpoint := "{YOUR_INSTANCE}.s3.titancloudstorage.com"
accessKeyID := ""
secretAccessKey := ""
useSSL := true
region := "us-west-1"
// Initialize a new MinIO client object.
titanClient, err := minio.New(endpoint, &minio.Options{
Creds: credentials.NewStaticV4(accessKeyID, secretAccessKey, ""),
Secure: useSSL,
Region: region,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}log.Printf("%#v
", titanClient) // titanClient is now setup
log.Printf("Connection created successfully!!!!!!!!!") // titanClient is now setup
}
Run Command:
go run .
2. Check if a bucket exists on Titan Cloud
The below code snippets checks if a bucket exists on the server. It returns True if the bucket exists.General Method:
BucketExists(ctx context.Context, bucketName string) (found bool, err error)
Code File:
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"github.com/minio/minio-go/v7"
"github.com/minio/minio-go/v7/pkg/credentials")
func main() {
// Set up credentials and endpoint for Titan Cloud Storage.
endpoint := "{YOUR_INSTANCE}.s3.titancloudstorage.com"
accessKeyID := ““
secretAccessKey := ""
useSSL := true
region := "us-west-1"
// Initialize a new MinIO client object.
titanClient, err := minio.New(endpoint, &minio.Options{
Creds: credentials.NewStaticV4(accessKeyID, secretAccessKey, ""),
Secure: useSSL,
Region: region,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
// Set the name of the bucket you want to check.
bucketName := "my-bucket"
// Check if the bucket exists.
exists, err := titanClient.BucketExists(context.Background(), bucketName)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
if exists {
log.Printf("Bucket '%s' exists.", bucketName)
} else {
log.Printf("Bucket '%s' does not exist.", bucketName)
}}
Run Command:
go run .
3. Create a bucket on Titan Cloud
The below code snippets create a bucket on the Titan Cloud server.General Method:
MakeBucket(ctx context.Context, bucketName string, opts MakeBucketOptions)
6. Remove Empty bucket on Titan Cloud
Code File:
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"github.com/minio/minio-go/v7"
"github.com/minio/minio-go/v7/pkg/credentials")
func main() {
// Set up credentials and endpoint for Titan Cloud Storage.
endpoint := "{YOUR_INSTANCE}.s3.titancloudstorage.com"
accessKeyID := ““
secretAccessKey := ""
useSSL := true
region := "us-west-1"
// Initialize a new MinIO client object.
titanClient , err := minio.New(endpoint, &minio.Options{
Creds: credentials.NewStaticV4(accessKeyID, secretAccessKey, ""),
Secure: useSSL,
Region: region,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
// Set the name of the bucket you want to create.
bucketName := "go-new-bucket"
// Check if the bucket already exists.
found, err := titanClient .BucketExists(context.Background(), bucketName)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
// If the bucket doesn't exist, create it.
if !found {
err = titanClient .MakeBucket(context.Background(), bucketName, minio.MakeBucketOptions{})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
log.Printf("Bucket '%s' created successfully.", bucketName)
} else {
log.Printf("Bucket '%s' already exists.", bucketName)
}}
Run Command:
go run .
4. Remove an empty bucket with Titan Cloud Storage
The below code snippets deletes the specified S3 bucket. Before the bucket can be deleted, all of the objects in it, including all versions and delete markers, must be deleted on a Titan Cloud.
General Method:
RemoveBucket(ctx context.Context, bucketName string) error
Code File:
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"github.com/minio/minio-go/v7"
"github.com/minio/minio-go/v7/pkg/credentials"
)
func main() {
// Set up credentials and endpoint for Titan Cloud Storage.
endpoint := "{YOUR_INSTANCE}.s3.titancloudstorage.com"
accessKeyID := ““
secretAccessKey := ""
useSSL := true
region := "us-west-1"
// Initialize a new MinIO client object.
titanClient , err := minio.New(endpoint, &minio.Options{
Creds: credentials.NewStaticV4(accessKeyID, secretAccessKey, ""),
Secure: useSSL,
Region: region,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
// Set the name of the bucket you want to delete.
bucketName := "go-new-bucket"
// Check if the bucket exists.
found, err := titanClient.BucketExists(context.Background(), bucketName)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
// If the bucket exists, check if it is empty.
if found {
objects := titanClient.ListObjects(context.Background(), bucketName, minio.ListObjectsOptions{})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
if len(objects) > 0 {
log.Printf("Bucket '%s' is not empty and cannot be deleted.", bucketName)
return
}
} else {
log.Printf("Bucket '%s' does not exist.", bucketName)
return
}
// If the bucket exists and is empty, delete it.
err = titanClient.RemoveBucket(context.Background(), bucketName)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
log.Printf("Bucket '%s' deleted successfully.", bucketName)}
Run Command:
go run .
5. List buckets on Titan Cloud Storage
The below code snippets shows all the accessible buckets information on a Titan Cloud.General Method:
ListBuckets(ctx context.Context) ([]BucketInfo, error)
Code File:
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"github.com/minio/minio-go/v7"
"github.com/minio/minio-go/v7/pkg/credentials")
func main() {
// Set up credentials and endpoint for Titan Cloud Storage.
endpoint := "{YOUR_INSTANCE}.s3.titancloudstorage.com"
accessKeyID := ““
secretAccessKey := ""
useSSL := true
region := "us-west-1"
// Initialize a new MinIO client object.
titanClient , err := minio.New(endpoint, &minio.Options{
Creds: credentials.NewStaticV4(accessKeyID, secretAccessKey, ""),
Secure: useSSL,
Region: region,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
// List all buckets in the account.
buckets, err := titanClient.ListBuckets(context.Background())
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
// Print the name of each bucket.
for _, bucket := range buckets {
log.Println(bucket.Name)
}}
Run Command:
go run .
6. Get bucket location, bucket object count and bucket size on Titan Cloud
The below code snippets shows three features of bucket information on a Titan Cloud.
- Get Bucket Location
- Get Bucket Count
- Get Bucket Size
1. Get bucket location
In MinIO, "Get bucket location" refers to retrieving the location or region of the specified bucket. Here's an example of how to use the following code to get the location of the bucket that exist on the Titan Cloud Storage server using the AWS SDK for Go(Golang).
Code File:
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"github.com/minio/minio-go/v7"
"github.com/minio/minio-go/v7/pkg/credentials")
func main() {
// Set up credentials and endpoint for Titan Cloud Storage.
endpoint := "{YOUR_INSTANCE}.s3.titancloudstorage.com"
accessKeyID := ““
secretAccessKey := ""
useSSL := true
region := "us-west-1"
// Initialize a new MinIO client object.
titanClient, err := minio.New(endpoint, &minio.Options{
Creds: credentials.NewStaticV4(accessKeyID, secretAccessKey, ""),
Secure: useSSL,
Region: region,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
// Set the name of the bucket you want to check.
bucketName := "my-bucket"
// Get the location of the bucket.
location, err := titanClient.GetBucketLocation(context.Background(), bucketName)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
log.Printf("Bucket '%s' is located in '%s'.", bucketName, location)}
Run Command:
go run .
2. Get bucket count
"Bucket object count" refers to the total number of objects stored in the bucket. Here's an example of how to use the following code to get the bucket object count the Titan Cloud Storage server using the AWS SDK for Go(Golang).
Code File:
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"github.com/minio/minio-go/v7"
"github.com/minio/minio-go/v7/pkg/credentials")
func main() {
// Set up credentials and endpoint for Titan Cloud Storage.
endpoint := "{YOUR_INSTANCE}.s3.titancloudstorage.com"
accessKeyID := ““
secretAccessKey := ""
useSSL := true
region := "us-west-1"
// Initialize a new MinIO client object.
titanClient, err := minio.New(endpoint, &minio.Options{
Creds: credentials.NewStaticV4(accessKeyID, secretAccessKey, ""),
Secure: useSSL,
Region: region,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
// Set the name of the bucket you want to get the object count for.
bucketName := "my-bucket"
// Initialize a count variable.
var count int
// List objects in the bucket and increment the count for each object.
objectCh := titanClient.ListObjects(context.Background(), bucketName, minio.ListObjectsOptions{})
for range objectCh {
count++
}
log.Printf("Bucket '%s' contains %d objects.", bucketName, count)}
Run Command:
go run .
3. Get bucket size
"Bucket size" refers to the total size of all objects stored in the bucket. This can be calculated by adding up the size of each object in the bucket. Here's an example of how to use the following code to get the size of the bucket on the Titan Cloud Storage server using the AWS SDK for Go(Golang).
Code File:
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"github.com/minio/minio-go/v7"
"github.com/minio/minio-go/v7/pkg/credentials")
func main() {
// Set up credentials and endpoint for Titan Cloud Storage.
endpoint := "{YOUR_INSTANCE}.s3.titancloudstorage.com"
accessKeyID := ““
secretAccessKey := ""
useSSL := true
region := "us-west-1"
// Initialize a new MinIO client object.
titanClient, err := minio.New(endpoint, &minio.Options{
Creds: credentials.NewStaticV4(accessKeyID, secretAccessKey, ""),
Secure: useSSL,
Region: region,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
// Set the name of the bucket you want to get the size of.
bucketName := "aws-bucket"
// Get the total size of the objects in the bucket.
objectStats, err := titanClient.StatObject(context.Background(), bucketName, "cat - three.jpg", minio.StatObjectOptions{})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
bucketSize := objectStats.Size
fmt.Printf("Bucket '%s' size is %d bytes
", bucketName, bucketSize)}
Run Command:
go run .
Object operations
Object operations refer to the various actions that can be performed on individual objects stored within a bucket in object storage systems. Some common object operations include:
• Put Object: This operation is used to upload a new object to a bucket or replace an existing object with a new version.
• Get Object: This operation is used to retrieve an object from a bucket and download it to a local machine.
• Delete Object: This operation is used to delete an object from a bucket.
• Delete Multiple Objects: This operation is used to delete many objects from a bucket.
• List Objects: This operation is used to retrieve a list of objects within a bucket.
• Copy Object: This operation is used to make a copy of an existing object within the same bucket or in a different bucket.
• Check Object Existence: This operation is used to check if an object exists in a bucket or not.
1. Copy object to a bucket on Titan Cloud Storage
The code snippets below show how to copy object using AWS SDK for Go(Golang) from a bucket on a Titan Cloud Storage service. Create or replace an object through server-side copying of an existing object. It supports conditional copying, copying a part of an object and server-side encryption of destination and decryption of source.General Method:
CopyObject(ctx context.Context, dst CopyDestOptions, src CopySrcOptions) (UploadInfo, error)
Code File:
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"os"
"github.com/minio/minio-go/v7"
"github.com/minio/minio-go/v7/pkg/credentials")
func main() {
// Set up credentials and endpoint for Titan Cloud Storage.
endpoint := "{YOUR_INSTANCE}.s3.titancloudstorage.com"
accessKeyID := ““
secretAccessKey := ""
useSSL := true
region := "us-west-1"
// Initialize a new MinIO client object.
titanClient , err := minio.New(endpoint, &minio.Options{
Creds: credentials.NewStaticV4(accessKeyID, secretAccessKey, ""),
Secure: useSSL,
Region: region,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
// Set the name of the source bucket and object you want to copy.
sourceBucket := "my-bucket"
sourceObject := "cat - two.jpg"
// Set the name of the destination bucket and object you want to copy to.
destinationBucket := "aws-bucket"
destinationObject := "cat - three.jpg"
// Copy the object to the destination bucket with a new name.
_, err = titanClient.CopyObject(context.Background(), minio.CopyDestOptions{
Bucket: destinationBucket,
Object: destinationObject,}, minio.CopySrcOptions{
Bucket: sourceBucket,
Object: sourceObject,})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
// Get the current working directory.
currentDir, err := os.Getwd()
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
// Set the path of the file you want to save the object to.
filePath := currentDir + "/" + destinationObject
// Download the object from the destination bucket.
err = titanClient.FGetObject(context.Background(), destinationBucket, destinationObject, filePath, minio.GetObjectOptions{})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
log.Printf("Object '%s' copied successfully from bucket '%s' to bucket '%s' with name '%s'
, and downloaded to '%s'.", sourceObject, sourceBucket, destinationBucket, destinationObject, filePath)}Run Command:
go run .
2. Check Object Existence in a bucket on Titan Cloud Storage
The code snippets below show how to check object existence using AWS SDK for Go(Golang) from a bucket on a Titan Cloud Storage service.General Method:
StatObject(ctx context.Context, bucketName, objectName string, opts StatObjectOptions) (ObjectInfo, error)
Code File:
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"github.com/minio/minio-go/v7"
"github.com/minio/minio-go/v7/pkg/credentials")
func main() {
// Set up credentials and endpoint for Titan Cloud Storage.
endpoint := "{YOUR_INSTANCE}.s3.titancloudstorage.com"
accessKeyID := ““
secretAccessKey := ""
useSSL := true
region := "us-west-1"
// Initialize a new MinIO client object.
titanClient, err := minio.New(endpoint, &minio.Options{
Creds: credentials.NewStaticV4(accessKeyID, secretAccessKey, ""),
Secure: useSSL,
Region: region,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
// Set the name of the bucket and object you want to check.
bucketName := "aws-bucket"
objectName := "text.txt"
// Check if the object exists in the bucket.
_, err = titanClient.StatObject(context.Background(), bucketName, objectName, minio.StatObjectOptions{})
if err != nil {
if minio.ToErrorResponse(err).StatusCode == 404 {
log.Printf("Object '%s' does not exist in bucket '%s'.", objectName, bucketName)
} else {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
} else {
log.Printf("Object '%s' exists in bucket '%s'.", objectName, bucketName)
}}
Run Command:
go run .
3. Put Object from a bucket on Titan Cloud
The code snippets below show how to put files from a bucket on a Titan Cloud. The PutObject method is a function provided by the MinIO Go client library that is used to upload an object to a bucket in a Titan Cloud storage service.General Method:
PutObject(ctx context.Context, bucketName, objectName string, reader io.Reader, objectSize int64,opts PutObjectOptions) (info UploadInfo, err error)
Note: Uploads objects that are less than 128MiB in a single PUT operation. For objects that are greater than 128MiB in size, PutObject seamlessly uploads the object as parts of 128MiB or more depending on the actual file size. The max upload size for an object is 5TB.
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"os"
"github.com/minio/minio-go/v7"
"github.com/minio/minio-go/v7/pkg/credentials"
)
func main() {
// Set up credentials and endpoint for Titan Cloud Storage.
endpoint := "{YOUR_INSTANCE}.s3.titancloudstorage.com"
accessKeyID := ““
secretAccessKey := ""
useSSL := true
region := "us-west-1"
// Initialize a new MinIO client object.
titanClient, err := minio.New(endpoint, &minio.Options{
Creds: credentials.NewStaticV4(accessKeyID, secretAccessKey, ""),
Secure: useSSL,
Region: region,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
// Set the name of the bucket and object you want to upload.
bucketName := "my-bucket"
objectName := "text.txt"
contentType := "text/plain"
// Open the file to be uploaded.
file, err := os.Open(objectName)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
defer file.Close()
// Get the file information.
fileInfo, err := file.Stat()
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
// Set the object options.
objectOptions := minio.PutObjectOptions{
ContentType: contentType,
}
// Upload the file to the bucket.
_, err = titanClient.PutObject(context.Background(), bucketName, objectName, file, fileInfo.Size(), objectOptions)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
log.Printf("Object '%s' uploaded successfully to bucket '%s'.", objectName, bucketName)}
Run Command:
go run .
4. Get Object from a bucket on Titan Cloud
The code snippets below show how to get object from a bucket on a Titan Cloud. In the MinIO Go library, the GetObject method is used to retrieve an object from a bucket in the titan cloud storage service.General Method:
GetObject(ctx context.Context, bucketName, objectName string, opts GetObjectOptions) (*Object, error)
Code File:
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"os"
"io"
"github.com/minio/minio-go/v7"
"github.com/minio/minio-go/v7/pkg/credentials"
)
func main() {
// Set up credentials and endpoint for Titan Cloud Storage.
endpoint := "{YOUR_INSTANCE}.s3.titancloudstorage.com"
accessKeyID := ““
secretAccessKey := ""
useSSL := true
region := "us-west-1"
// Initialize a new MinIO client object.
titanClient , err := minio.New(endpoint, &minio.Options{
Creds: credentials.NewStaticV4(accessKeyID, secretAccessKey, ""),
Secure: useSSL,
Region: region,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
// Set the name of the bucket and object you want to download.
bucketName := "my-bucket"
objectName := "cat - two.jpg"
// Get information about the object.
object, err := titanClient.GetObject(context.Background(), bucketName, objectName, minio.GetObjectOptions{})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
defer object.Close()
// Create a new file to write the object contents to.
file, err := os.Create(objectName)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
defer file.Close()
// Write the object contents to the file.
if _, err = io.Copy(file, object); err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
log.Printf("Object '%s' downloaded successfully.", objectName)}
Run Command:
go run .
5. List all the objects in the bucket on Titan Cloud
The code snippets below show how to list the items' details, optionally including bucket versions created on a Titan Cloud.General Method:
ListObjects(ctx context.Context, bucketName string, opts ListObjectsOptions) <-chan ObjectInfo
Code File:
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"github.com/minio/minio-go/v7"
"github.com/minio/minio-go/v7/pkg/credentials")
func main() {
// Set up credentials and endpoint for Titan Cloud Storage.
endpoint := "{YOUR_INSTANCE}.s3.titancloudstorage.com"
accessKeyID := ““
secretAccessKey := ""
useSSL := true
region := "us-west-1"
// Initialize a new MinIO client object.
titanClient, err := minio.New(endpoint, &minio.Options{
Creds: credentials.NewStaticV4(accessKeyID, secretAccessKey, ""),
Secure: useSSL,
Region: region,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
// Set the name of the bucket you want to list objects for.
bucketName := "my-bucket"
// List all objects in the bucket.
objectCh := titanClient.ListObjects(context.Background(), bucketName, minio.ListObjectsOptions{})
for object := range objectCh {
if object.Err != nil {
log.Fatalln(object.Err)
}
fmt.Println(object.Key, object.Size, object.LastModified)
}}Run Command:
go run .
6. Remove an object from bucket on Titan Cloud
The below code snippets remove an object from the bucket information on a Titan Cloud.General Method:RemoveObject(ctx context.Context, bucketName, objectName string, opts minio.RemoveObjectOptions) error
Code File:
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"github.com/minio/minio-go/v7"
"github.com/minio/minio-go/v7/pkg/credentials")
func main() {
// Set up credentials and endpoint for Titan Cloud Storage.
endpoint := "{YOUR_INSTANCE}.s3.titancloudstorage.com"
accessKeyID := ““
secretAccessKey := ""
useSSL := true
region := "us-west-1"
// Initialize a new MinIO client object.
titanClient , err := minio.New(endpoint, &minio.Options{
Creds: credentials.NewStaticV4(accessKeyID, secretAccessKey, ""),
Secure: useSSL,
Region: region,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
// Set the name of the bucket and object you want to delete.
bucketName := "aws-bucket"
objectName := "text.txt"
// Delete the object from the bucket.
err = titanClient.RemoveObject(context.Background(), bucketName, objectName, minio.RemoveObjectOptions{})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
log.Printf("Object '%s' deleted successfully from bucket '%s'.", objectName, bucketName)}
Run Command:
go run .
7. Remove multiple objects from bucket on Titan Cloud
7. Remove multiple objects from bucket on Titan Cloud
The code snippets below show how to delete numerous objects from the bucket simultaneously on a Titan Cloud. It removes a list of objects obtained from an input channel. The call sends a delete request to the server up to 1000 objects at a time. The errors observed are sent over the error channel.
General Method:
RemoveObjects(ctx context.Context, bucketName string, objectsCh <-chan ObjectInfo, opts RemoveObjectsOptions) <-chan RemoveObjectError
Code File:
package main
import (
"context"
"log""github.com/minio/minio-go/v7" "github.com/minio/minio-go/v7/pkg/credentials")
func main() {
// Set up credentials and endpoint for Titan Cloud Storage.
endpoint := "{YOUR_INSTANCE}.s3.titancloudstorage.com"
accessKeyID := ““
secretAccessKey := ""
useSSL := true
region := "us-west-1"// Initialize a new MinIO client object. titanClient, err := minio.New(endpoint, &minio.Options{ Creds: credentials.NewStaticV4(accessKeyID, secretAccessKey, ""), Secure: useSSL, Region: region, }) if err != nil { log.Fatalln(err) } // Set the name of the bucket and object names you want to remove. bucketName := "my-bucket" objectNames := []string{"text.txt", "mytext.txt", "my-new-file.txt"} // Create a slice of minio.ObjectInfo objects to represent the objects to remove. objects := make([]minio.ObjectInfo, len(objectNames)) for i, objectName := range objectNames { object, err := titanClient.StatObject(context.Background(), bucketName, objectName, minio.StatObjectOptions{}) if err != nil { log.Fatalln(err) } objects[i] = object } // Convert the objects slice to a channel. objectCh := make(chan minio.ObjectInfo) go func() { defer close(objectCh) for _, object := range objects { objectCh <- object } }() // Remove the objects from the bucket. deletedObjects := titanClient.RemoveObjects(context.Background(), bucketName, objectCh, minio.RemoveObjectsOptions{}) for deletedObject := range deletedObjects { if deletedObject.Err != nil { log.Fatalln(deletedObject.Err) } log.Printf("Object '%s' deleted successfully from bucket '%s'.", bucketName) } log.Printf("Objects deleted successfully from bucket '%s'.", bucketName)
}
Run Command:
go run .
File Object Operations
In MinIO Go SDK, the file object operations include the following:
• FPutObject - Uploads a file to a bucket.
• FGetObject - Downloads an object from a bucket to a file.
1. Uploads contents from a file to objectName on Titan Cloud Storage
The code snippets below show how to show how to upload contents from a file to objectName using AWS SDK for Go(Golang) from a bucket on a Titan Cloud Storage service.General Method:
FPutObject(ctx context.Context, bucketName, objectName, filePath, opts PutObjectOptions) (info UploadInfo, err error)
Code File:
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"os""github.com/minio/minio-go/v7" "github.com/minio/minio-go/v7/pkg/credentials")
func main() {
// Set up credentials and endpoint for Titan Cloud Storage.
endpoint := "{YOUR_INSTANCE}.s3.titancloudstorage.com"
accessKeyID := ““
secretAccessKey := ""
useSSL := true
region := "us-west-1"// Initialize a new MinIO client object. titanClient, err := minio.New(endpoint, &minio.Options{ Creds: credentials.NewStaticV4(accessKeyID, secretAccessKey, ""), Secure: useSSL, Region: region, }) if err != nil { log.Fatalln(err) } // Set the name of the bucket and object you want to upload. bucketName := "my-bucket" objectName := "text.txt" // Open the file to upload. file, err := os.Open(objectName) if err != nil { log.Fatalln(err) } defer file.Close() // Get the file information, including its size. fileStat, err := file.Stat() if err != nil { log.Fatalln(err) } fileSize := fileStat.Size() // Upload the file to the bucket. _, err = titanClient.FPutObject(context.Background(), bucketName, objectName, file.Name(), minio.PutObjectOptions{ContentType: "application/octet-stream"}) if err != nil { log.Fatalln(err) } log.Printf("File '%s' uploaded successfully to bucket '%s'. Size: %d bytes.", objectName, bucketName, fileSize)}
Run Command:
go run .
2. Downloads and saves the object as a file in the local filesystem on Titan Cloud Storage
The code snippets below show how to show downloading and saving the object as a file in the local filesystem using the AWS SDK for Go (Golang) from a bucket on a Titan Cloud Storage service.General Method:
FGetObject(ctx context.Context, bucketName, objectName, filePath string, opts GetObjectOptions) error
Code File:
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"os""github.com/minio/minio-go/v7" "github.com/minio/minio-go/v7/pkg/credentials")
func main() {
// Set up credentials and endpoint for Titan Cloud Storage.
endpoint := "{YOUR_INSTANCE}.s3.titancloudstorage.com"
accessKeyID := ““
secretAccessKey := ""
useSSL := true
region := "us-west-1"// Initialize a new MinIO client object. titanClient, err := minio.New(endpoint, &minio.Options{ Creds: credentials.NewStaticV4(accessKeyID, secretAccessKey, ""), Secure: useSSL, Region: region, }) if err != nil { log.Fatalln(err) } // Set the name of the bucket and object you want to download. bucketName := "my-bucket" objectName := "text.txt" // Get the current working directory. currentDir, err := os.Getwd() if err != nil { log.Fatalln(err) } // Set the path of the file you want to save the object to. filePath := currentDir + "/download/" + objectName // Download the object from the bucket. err = titanClient.FGetObject(context.Background(), bucketName, objectName, filePath, minio.GetObjectOptions{}) if err != nil { log.Fatalln(err) } log.Printf("Object '%s' downloaded successfully to '%s'.", objectName, filePath)}
Run Command:
go run .
